LiteServer backup vps70253415 Debian 10 (HDD 512Go) borg + audio gonic - xoyaz.xyz
Liteserver

LiteServer backup vps70253415 ARRETE DEFINITIVEMENT le 24 septembre 2021
LiteServer est votre partenaire pour une connectivité réseau de qualité. Nous avons les routes les plus courtes et les plus rapides vers des milliers de réseaux mondiaux. Nous avons des POP dans plusieurs pays avec une connectivité aux points d’échange locaux pour acheminer le trafic aussi efficacement que possible. Notre réseau est rapide et évolutif à tout moment.
KVM Debian Buster
vps70253415
Status Online
IPv4 Address 1
IP Address 5.2.79.127
Virtualization Type (KVM)
Hostname vps70253415
Node NL-DRN-KVMHDD-13
Operating System Debian 10.1.0 - Minimal (64-bit)
IPv6 Address 1
Disk Space 512 GB
Bandwidth 6 TB
Memory 1 GB
Swap -
Installer le noyau 5.7 (facultatif)
A partir du noyau 5.6 a le module wireguard est intégré
ssh root@5.2.79.127
Exécuter les commandes suivantes
1
2
3
4
echo "deb http://deb.debian.org/debian/ unstable main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/unstable-wireguard.list
printf 'Package: *\nPin: release a=unstable\nPin-Priority: 90\n' | sudo tee /etc/apt/preferences.d/limit-unstable
apt update && apt upgrade
apt install linux-image-5.7.0-1-amd64
Redémarrer la machine et vérifier
1
2
systemctl reboot
uname -a
Linux vps70253415 5.7.0-1-amd64 #1 SMP Debian 5.7.6-1 (2020-06-24) x86_64 GNU/Linux
Connexion root
1
ssh root@5.2.79.127
Changement mot de passe
1
passwd root
Mise à jour
1
apt update && apt upgrade
Installer utilitaires
1
apt install rsync curl tmux jq figlet git mailutils dnsutils p7zip-full -y
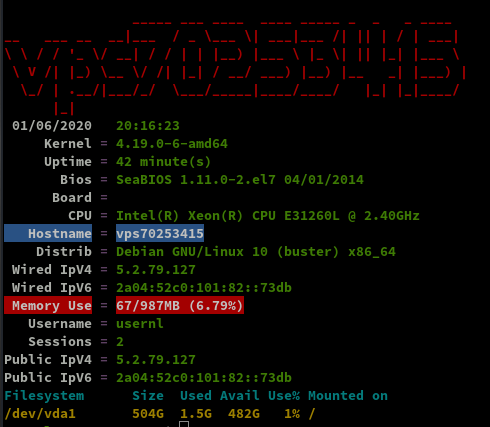
Hostname
1
hostnamectl
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Static hostname: vps70253415
Icon name: computer-vm
Chassis: vm
Machine ID: bc596acea5de2e7255c0f5f7f6db3946
Boot ID: c4deac0e19e047999cf65fa83d97ca8e
Virtualization: kvm
Operating System: Debian GNU/Linux 10 (buster)
Kernel: Linux 4.19.0-6-amd64
Architecture: x86-64
Europe/Paris (TimeZone tzdata)
Europe/Amsterdam
1
dpkg-reconfigure tzdata
1
2
3
Current default time zone: 'Europe/Amsterdam'
Local time is now: Wed Jun 10 14:01:44 CEST 2020.
Universal Time is now: Wed Jun 10 12:01:44 UTC 2020.
Adresse IPV4 IPV6
Le paramétrage réseau
1
/etc/network/interfaces
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
# The loopback network interface
auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
# The primary network interface
auto eth0
iface eth0 inet static
address 5.2.79.127
netmask 255.255.255.0
gateway 5.2.79.1
iface eth0 inet6 static
accept_ra 0
address 2a04:52c0:101:82::1
netmask 64
gateway 2a04:52c0:0101:0000:0000:0000:0000:0001
post-up /sbin/ip -r route add 2a04:52c0:0101:0000:0000:0000:0000:0001 dev eth0
post-up /sbin/ip -r route add default via 2a04:52c0:0101:0000:0000:0000:0000:0001
Après modification du paramétrage réseau, un redémarrage est nécessaire
Le réseau après redémarrage
1
ip a
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 ::1/128 scope host
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
2: eth0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 00:16:3c:a9:4f:7e brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 5.2.79.127/24 brd 5.2.79.255 scope global eth0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 2a04:52c0:101:82::1/64 scope global
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::216:3cff:fea9:4f7e/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
Création utilisateur
Utilisateur usernl
1
useradd -m -d /home/usernl/ -s /bin/bash usernl
Mot de passe usernl
1
passwd usernl
Visudo pour les accès root via utilisateur usernl
1
2
apt install sudo
echo "usernl ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: ALL" >> /etc/sudoers
Déconnexion puis connexion ssh en mode utilisateur
1
ssh usernl@5.2.79.127
OpenSSH, clé et script

connexion avec clé
sur l'ordinateur de bureau
Générer une paire de clé curve25519-sha256 (ECDH avec Curve25519 et SHA2) pour une liaison SSH avec le serveur.
1
ssh-keygen -t ed25519 -o -a 100 -f ~/.ssh/OVZ-STORAGE-128
Envoyer les clés publiques sur le serveur KVM
1
scp ~/.ssh/OVZ-STORAGE-128.pub usernl@5.2.79.127:/home/usernl/
sur le serveur KVM On se connecte
1
ssh usernl@5.2.79.127
Copier le contenu de la clé publique dans /home/$USER/.ssh/authorized_keys
1
cd ~
Sur le KVM ,créer un dossier .ssh
1
2
mkdir .ssh
cat $HOME/OVZ-STORAGE-128.pub >> $HOME/.ssh/authorized_keys
et donner les droits
1
chmod 600 $HOME/.ssh/authorized_keys
effacer le fichier de la clé
1
rm $HOME/*.pub
Modifier la configuration serveur SSH
1
sudo nano /etc/ssh/sshd_config
Modifier
1
2
3
Port = 55036
PermitRootLogin no
PasswordAuthentication no
session SSH ne se termine pas correctement lors d'un "reboot" à distance
Si vous tentez de redémarrer/éteindre une machine distance par ssh, vous pourriez constater que votre session ne se termine pas correctement, vous laissant avec un terminal inactif jusqu’à l’expiration d’un long délai d’inactivité. Il existe un bogue 751636 à ce sujet. Pour l’instant, la solution de contournement à ce problème est d’installer :
1
sudo apt-get install libpam-systemd
cela terminera la session ssh avant que le réseau ne tombe.
Veuillez noter qu’il est nécessaire que PAM soit activé dans sshd.
Relancer openSSH
1
sudo systemctl restart sshd
Accès depuis le poste distant avec la clé privée
1
ssh usernl@5.2.79.127 -p 55036 -i /home/yannick/.ssh/OVZ-STORAGE-128 # choix par défaut ,pour la compatibilité avec l'ancien serveur de sauvegarde de 128Go
Outils, scripts motd et ssh_rc_bash
Motd
1
sudo rm /etc/motd && sudo nano /etc/motd
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
____ __ ___ ___ ____ _ _ _ ___
__ __ _ __ ___|__ |/ \|_ )| __||__ /| | | / || __|
\ V /| '_ \(_-< / /| () |/ / |__ \ |_ \|_ _|| ||__ \
\_/ | .__//__/ /_/ \__//___||___/|___/ |_| |_||___/
__|_| ___ ____ ___ _ ___ ____
| __| |_ ) |__ |/ _ \ / ||_ )|__ |
|__ \ _ / / _ / / \_, /_ | | / / / /
|___/(_)/___|(_)/_/ /_/(_)|_|/___| /_/
Script ssh_rc_bash
ATTENTION!!! Les scripts sur connexion peuvent poser des problèmes pour des appels externes autres que ssh
1
2
3
wget https://yann.cinay.eu/files/ssh_rc_bash
chmod +x ssh_rc_bash # rendre le bash exécutable
./ssh_rc_bash # exécution
Parefeu
Choix entre ufw et iptables (problématique avec wireguard)
Parefeu UFW
UFW, ou pare - feu simple , est une interface pour gérer les règles de pare-feu dans Arch Linux, Debian ou Ubuntu. UFW est utilisé via la ligne de commande (bien qu’il dispose d’interfaces graphiques disponibles), et vise à rendre la configuration du pare-feu facile.
Installation Debian / Ubuntu
1
sudo apt-get install ufw
Par défaut, les jeux de règles d’UFW sont vides, de sorte qu’il n’applique aucune règle de pare-feu, même lorsque le démon est en cours d’exécution.
Les règles
1
2
3
4
5
sudo ufw allow 55036/tcp # port SSH
sudo ufw allow http # port 80
sudo ufw allow https # port 443
sudo ufw allow DNS # port 53
sudo ufw allow 51820/udp # wireguard
Activer le parefeu
1
sudo ufw enable
1
2
Command may disrupt existing ssh connections. Proceed with operation (y|n)? y
Firewall is active and enabled on system startup
Status
1
sudo ufw status verbose
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
Status: active
Logging: on (low)
Default: deny (incoming), allow (outgoing), deny (routed)
New profiles: skip
To Action From
-- ------ ----
55036/tcp ALLOW IN Anywhere
80/tcp ALLOW IN Anywhere
443/tcp ALLOW IN Anywhere
53 (DNS) ALLOW IN Anywhere
51820/udp ALLOW IN Anywhere
55036/tcp (v6) ALLOW IN Anywhere (v6)
80/tcp (v6) ALLOW IN Anywhere (v6)
443/tcp (v6) ALLOW IN Anywhere (v6)
53 (DNS (v6)) ALLOW IN Anywhere (v6)
51820/udp (v6) ALLOW IN Anywhere (v6)
iptables

On utilise un service systemd
Créer le fichier le script /sbin/iptables-firewall.sh
1
sudo nano /sbin/iptables-firewall.sh
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
#!/bin/bash
# Configure iptables firewall
# Limit PATH
PATH="/sbin:/usr/sbin:/bin:/usr/bin"
# iptables configuration
firewall_start() {
###################
# IPv4 #
###################
# refuser input et forward par défaut, accepter output
iptables -t filter -P INPUT DROP
iptables -t filter -P FORWARD DROP
iptables -t filter -P OUTPUT ACCEPT
# interface lo (loop) accessible
iptables -A INPUT -i lo -j ACCEPT
iptables -A OUTPUT -o lo -j ACCEPT
# maintenir les connexions établies
iptables -A INPUT -m state --state RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
iptables -A OUTPUT -m state --state RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
# accepter en entrée le ping (icmp), et les
# connexions sur les ports nécessaires.
iptables -A INPUT -p icmp --icmp-type echo-request -m conntrack --ctstate NEW -m limit --limit 1/s --limit-burst 1 -j ACCEPT
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 55036 -j ACCEPT
# accepter en sortie le ping, les requêtes HTTP(S), DNS,
# et les connexions sur les ports nécessaires.
iptables -A OUTPUT -p icmp --icmp-type echo-request -m conntrack --ctstate NEW -j ACCEPT
iptables -A OUTPUT -p udp --dport 53 -j ACCEPT
iptables -A OUTPUT -p tcp --dport 53 -j ACCEPT
# wireguard
iptables -A INPUT -p udp --dport 51820 -j ACCEPT
# HTTP + HTTPS Out
iptables -t filter -A OUTPUT -p tcp --dport 80 -j ACCEPT
iptables -t filter -A OUTPUT -p tcp --dport 443 -j ACCEPT
# HTTP + HTTPS In
iptables -t filter -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 80 -j ACCEPT
iptables -t filter -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 443 -j ACCEPT
###################
# IPv6 #
###################
# refuser input et forward par défaut, accepter output
ip6tables -t filter -P INPUT DROP
ip6tables -t filter -P FORWARD DROP
ip6tables -t filter -P OUTPUT ACCEPT
# interface lo (loop) accessible
ip6tables -A INPUT -i lo -j ACCEPT
ip6tables -A OUTPUT -o lo -j ACCEPT
# maintenir les connexions établies
ip6tables -A INPUT -m state --state RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
ip6tables -A OUTPUT -m state --state RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
# accepter en entrée le ping (icmpv6), les
# connexions entrantes déjà établies et les connexions sur les ports nécessaires.
#ip6tables -A INPUT -p icmpv6 --icmpv6-type echo-request -m conntrack --ctstate NEW -m limit --limit 1/s --limit-burst 1 -j ACCEPT
ip6tables -A INPUT -p icmpv6 -j ACCEPT
ip6tables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 55036 -j ACCEPT
# wireguard
ip6tables -A INPUT -p udp --dport 51820 -j ACCEPT
# HTTP + HTTPS Out
ip6tables -t filter -A OUTPUT -p tcp --dport 80 -j ACCEPT
ip6tables -t filter -A OUTPUT -p tcp --dport 443 -j ACCEPT
# HTTP + HTTPS In
ip6tables -t filter -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 80 -j ACCEPT
ip6tables -t filter -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 443 -j ACCEPT
# accepter en sortie le ping, les requêtes HTTP(S), DNS,
# et les connexions sur les ports nécessaires.
ip6tables -t filter -A OUTPUT -p icmpv6 --icmpv6-type echo-request -j ACCEPT
ip6tables -A OUTPUT -p udp --dport 53 -j ACCEPT
ip6tables -A OUTPUT -p tcp --dport 53 -j ACCEPT
}
# clear iptables configuration
firewall_stop() {
iptables -F
iptables -X
iptables -P INPUT ACCEPT
iptables -P FORWARD ACCEPT
iptables -P OUTPUT ACCEPT
ip6tables -F
ip6tables -X
ip6tables -P INPUT ACCEPT
ip6tables -P FORWARD ACCEPT
ip6tables -P OUTPUT ACCEPT
}
# execute action
case "$1" in
start|restart)
echo "Starting firewall"
firewall_stop
firewall_start
;;
stop)
echo "Stopping firewall"
firewall_stop
;;
esac
Les droits et exécutable
1
2
sudo chown root:root /sbin/iptables-firewall.sh
sudo chmod 750 /sbin/iptables-firewall.sh
Créer le service systemd iptables-firewall.service
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
cat << EOF | sudo tee /etc/systemd/system/iptables-firewall.service
[Unit]
Description=iptables firewall service
After=network.target
[Service]
Type=oneshot
ExecStart=/sbin/iptables-firewall.sh start
RemainAfterExit=true
ExecStop=/sbin/iptables-firewall.sh stop
StandardOutput=journal
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
EOF
Recharger systemd manager
1
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
Lancer le service iptables et l’activer
1
2
sudo systemctl start iptables-firewall # vérifier le fonctionnement avant de valider
sudo systemctl enable iptables-firewall
OVH configuration domaine xoyaz.xyz
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
$TTL 3600
@ IN SOA dns106.ovh.net. tech.ovh.net. (2021030200 86400 3600 3600000 300)
IN NS ns106.ovh.net.
IN NS dns106.ovh.net.
IN A 5.2.79.127
IN AAAA 2a04:52c0:101:82::1
wg IN CNAME xoyaz.xyz.
zic IN CNAME xoyaz.xyz.
wg : wireguard
zic: audio serveur
Certificats letsencrypt - xoyaz.xyz
Installation gestionnaire des certificats Let’s Encrypt
1
2
3
4
5
cd ~
sudo apt install socat # prérequis
git clone https://github.com/Neilpang/acme.sh.git
cd acme.sh
./acme.sh --install
Les clés OVH API
1
acme.sh --dns dns_ovh --issue --keylength ec-384 -d 'xoyaz.xyz' -d 'zic.xoyaz.xyz'
Résultat de l’installation
1
2
3
4
[Tue 02 Jun 2020 07:03:47 AM CEST] Your cert is in /home/usernl//.acme.sh/xoyaz.xyz_ecc/xoyaz.xyz.cer
[Tue 02 Jun 2020 07:03:47 AM CEST] Your cert key is in /home/usernl//.acme.sh/xoyaz.xyz_ecc/xoyaz.xyz.key
[Tue 02 Jun 2020 07:03:47 AM CEST] The intermediate CA cert is in /home/usernl//.acme.sh/xoyaz.xyz_ecc/ca.cer
[Tue 02 Jun 2020 07:03:47 AM CEST] And the full chain certs is there: /home/usernl//.acme.sh/xoyaz.xyz_ecc/fullchain.cer
Installation des certificats
1
2
3
sudo mkdir -p /etc/ssl/private/
sudo chown $USER -R /etc/ssl/private/
acme.sh --ecc --install-cert -d xoyaz.xyz -d 'zic.xoyaz.xyz' --key-file /etc/ssl/private/xoyaz.xyz-key.pem --fullchain-file /etc/ssl/private/xoyaz.xyz-fullchain.pem --reloadcmd 'sudo systemctl reload nginx.service'
Editer le crontab
1
crontab -e
1
56 0 * * * "/home/usernl/.acme.sh"/acme.sh --cron --home "/home/usernl/.acme.sh" --renew-hook "/home/usernl/.acme.sh/acme.sh --ecc --install-cert -d xoyaz.xyz --key-file /etc/ssl/private/xoyaz.xyz-key.pem --fullchain-file /etc/ssl/private/xoyaz.xyz-fullchain.pem --reloadcmd 'sudo systemctl reload nginx.service'" > /dev/null
Borgbackup xoyaz.xyz (5.2.79.127)
Conventions
- serveur backup : Serveur de sauvegarde borgbackup xoyaz.xyz (5.2.79.127)
On se connecte sur la machine
1
sudo apt update
Installer borgbackup
1
sudo apt install borgbackup
on passe en mode su
1
sudo -s
Créer un utilisateur borg dédié aux sauvegardes par BorgBackup :
1
2
mkdir -p /srv/data
useradd borg --create-home --home-dir /srv/data/borg-backups
Créer le dossier .ssh utilisateur “borg”
1
sudo -u borg mkdir /srv/data/borg-backups/.ssh
Créer le fichier authorized_keys
1
sudo -u borg touch /srv/data/borg-backups/.ssh/authorized_keys
Autoriser utilisateur borg à exécuter /usr/bin/borg uniquement
1
echo "borg ALL=NOPASSWD: /usr/bin/borg" >> /etc/sudoers
Nginx + PHP7.3
Nginx Light
modifier le fichier /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
On autorise tls1.2 et tls1.3 uniquement et ciphers off
1
2
3
4
[...]
ssl_protocols TLSv1.2 TLSv1.3;
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers off;
[...]
Accès dossier pour les fichiers de configuration
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
[...]
##
# Virtual Host Configs
##
include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;
# include /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/*;
[...]
PHP7.3
Installation
1
sudo apt install php7.3-fpm php7.3-sqlite3 php7.3-gd
xoyaz.xyz
Créer le fichier /etc/nginx/conf.d/xoyaz.xyz.conf
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
server {
listen 80;
listen [::]:80;
server_name xoyaz.xyz;
return 301 https://$host$request_uri;
}
server {
listen 443 ssl http2;
listen [::]:443 ssl http2;
server_name xoyaz.xyz;
ssl_certificate /etc/ssl/private/xoyaz.xyz-fullchain.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/ssl/private/xoyaz.xyz-key.pem;
root /var/www/;
index index/ index.php;
# TLS 1.3 only
ssl_protocols TLSv1.3;
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers off;
# HSTS (ngx_http_headers_module is required) (63072000 seconds)
add_header Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=63072000" always;
# OCSP stapling
ssl_stapling on;
ssl_stapling_verify on;
# verify chain of trust of OCSP response using Root CA and Intermediate certs
ssl_trusted_certificate /etc/ssl/private/xoyaz.xyz-fullchain.pem;
# fichiers de configuration
include /etc/nginx/conf.d/xoyaz.xyz.d/*.conf;
# replace with the IP address of your resolver
resolver 127.0.0.1;
}
Créer le sous-dossier
1
sudo mkdir /etc/nginx/conf.d/xoyaz.xyz.d/
Vérifier
1
sudo nginx -t
1
2
nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful
Recharger nginx
1
sudo systemctl reload nginx
Pour tester le php
1
echo "<?php phpinfo(); ?>" | sudo tee /var/www//info.php
https://xoyaz.xyz/info.php
Page d’accueil (facultatif)
Déposer une image dans le dossier /var/www/
Créer un fichier /var/www//index/
<!DOCTYPE/>
/>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Backup xoyaz.xyz</title>
<style type="text/css" media="screen" >
html {
margin:0;
padding:0;
background: url(wallpaper.jpg) no-repeat center fixed;
-webkit-background-size: cover; /* pour anciens Chrome et Safari */
background-size: cover; /* version standardisée */
}
body { color: white; }
a:link {
color: grey;
background-color: transparent;
text-decoration: none;
}
a {
text-decoration: underline;
background-color: transparent;
color: #a00;
}
a:visited {
color: #844;
}
a:hover, a:focus, a:active {
text-decoration: none;
color: white;
background: #800;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Serveur xoyaz.xyz</h1>
<p><a href="/transmission">Transmission</a>
<em> permet le téléchargement et la création de torrents.<br>Ce logiciel supporte les technologies décentralisées sans tracker, tel que PEX, DHT et les liens magnets.</em>
</p>
<p><a href="https://zic.xoyaz.xyz">Navidrome</a>
<em> Audio est compatible avec la majorité des clients subsoniques.<br>
Les clients android suivants sont testés et leur bon fonctionnement est confirmé :
<a href="https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=github.daneren2005.dsub">DSub</a>, <a href="https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=org.moire.ultrasonic">Ultrasons</a> et <a href="https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.ghenry22.mymusicstash">Stash de la musique</a></em>
</p>
</body>
</>
Lien https://xoyaz.xyz
Authentification 2FA
Authentification double facteur PHP TOTP
PHP - Portail d’authentification web authentification à deux facteurs (2FA).
TwoFactorAuth utilise PHP et des bibliothèques
- php 7.3 pour nginx
- La bibliothèque GD
- La bibliothèque SQLite3
Installation
1
2
3
4
sudo apt install php7.3-fpm php7.3-gd php7.3-sqlite3
git clone https://github.com/Arno0x/TwoFactorAuth.git twofactorauth
sudo mv twofactorauth /var/www//
sudo chown www-data.www-data -R /var/www//twofactorauth
Modifier ‘QRCODE_TITLE’,’SESSION_NAME’ et ‘AUTH_SUCCEED_REDIRECT_URL’ dans le fichier de configuration /var/www//twofactorauth/config.php
Ouvrir le lien https://xoyaz.xyz/twofactorauth/index.php
Créer l’administrateur “xoyaz”, son mot de passe et scanner le Qr Code avec une application TOTP
Transmission
Transmission permet le téléchargement et la création de torrents. Ce logiciel supporte les technologies décentralisées sans tracker, tel que PEX, DHT et les liens magnets.
Pour l’installation suivre ce lien :Debian Transmission
Ajout utilisateur courant au groupe “debian-transmission”
1
sudo usermod -a -G debian-transmission $USER
Accès sécurisé sur le site xoyaz.xyz/transmission avec login mot de passe et 2FA
On supprime le fichier de configuration ~/.config/transmission-daemon/settings.json
1
sudo rm ~/.config/transmission-daemon/settings.json
Modification du fichier de configuration /etc/transmission-daemon/settings.json
1
sudo systemctl stop transmission-daemon.service
Le fichier de configuration “transmission”
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
{
"alt-speed-down": 50,
"alt-speed-enabled": false,
"alt-speed-time-begin": 540,
"alt-speed-time-day": 127,
"alt-speed-time-enabled": false,
"alt-speed-time-end": 1020,
"alt-speed-up": 50,
"bind-address-ipv4": "0.0.0.0",
"bind-address-ipv6": "::",
"blocklist-enabled": false,
"blocklist-url": "http://www.example.com/blocklist",
"cache-size-mb": 4,
"dht-enabled": true,
"download-dir": "/home/usernl/torrent/complet",
"download-limit": 100,
"download-limit-enabled": 0,
"download-queue-enabled": true,
"download-queue-size": 5,
"encryption": 1,
"idle-seeding-limit": 30,
"idle-seeding-limit-enabled": false,
"incomplete-dir": "/home/usernl/torrent/encours",
"incomplete-dir-enabled": false,
"lpd-enabled": false,
"max-peers-global": 200,
"message-level": 1,
"peer-congestion-algorithm": "",
"peer-id-ttl-hours": 6,
"peer-limit-global": 200,
"peer-limit-per-torrent": 50,
"peer-port": 51413,
"peer-port-random-high": 65535,
"peer-port-random-low": 49152,
"peer-port-random-on-start": false,
"peer-socket-tos": "default",
"pex-enabled": true,
"port-forwarding-enabled": false,
"preallocation": 1,
"prefetch-enabled": true,
"queue-stalled-enabled": true,
"queue-stalled-minutes": 30,
"ratio-limit": 2,
"ratio-limit-enabled": false,
"rename-partial-files": true,
"rpc-authentication-required": false,
"rpc-bind-address": "0.0.0.0",
"rpc-enabled": true,
"rpc-host-whitelist": "",
"rpc-host-whitelist-enabled": false,
"rpc-password": "{2f217a20225338209def1c9fa5587751c6a608d8Onz8WkP5",
"rpc-port": 9091,
"rpc-url": "/transmission/",
"rpc-username": "yan",
"rpc-whitelist": "127.0.0.1",
"rpc-whitelist-enabled": false,
"scrape-paused-torrents-enabled": true,
"script-torrent-done-enabled": false,
"script-torrent-done-filename": "",
"seed-queue-enabled": false,
"seed-queue-size": 10,
"speed-limit-down": 100,
"speed-limit-down-enabled": false,
"speed-limit-up": 100,
"speed-limit-up-enabled": false,
"start-added-torrents": true,
"trash-original-torrent-files": false,
"umask": 7,
"upload-limit": 100,
"upload-limit-enabled": 0,
"upload-slots-per-torrent": 14,
"utp-enabled": true
}
Relancer transmission
1
sudo systemctl start transmission-daemon
Le fichier de configuration /etc/nginx/conf.d/xoyaz.xyz.conf
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
server {
listen 80;
listen [::]:80;
server_name xoyaz.xyz;
return 301 https://$host$request_uri;
}
server {
listen 443 ssl http2;
listen [::]:443 ssl http2;
server_name xoyaz.xyz;
ssl_certificate /etc/ssl/private/xoyaz.xyz-fullchain.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/ssl/private/xoyaz.xyz-key.pem;
root /var/www/;
index index/ index.php;
# TLS 1.3 only
ssl_protocols TLSv1.3;
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers off;
# HSTS (ngx_http_headers_module is required) (63072000 seconds)
add_header Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=63072000" always;
# OCSP stapling
ssl_stapling on;
ssl_stapling_verify on;
# verify chain of trust of OCSP response using Root CA and Intermediate certs
ssl_trusted_certificate /etc/ssl/private/xoyaz.xyz-fullchain.pem;
#PHP7.3
location ~ \.php$ {
fastcgi_split_path_info ^(.+\.php)(/.+)$;
fastcgi_pass unix:/run/php/php7.3-fpm.sock; # PHP7.3
fastcgi_index index.php;
include fastcgi_params;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
}
# fichiers de configuration
include /etc/nginx/conf.d/xoyaz.xyz.d/*.conf;
# replace with the IP address of your resolver
resolver 127.0.0.1;
location = /twofactorauth/login/login.php {
allow all;
auth_request off;
fastcgi_split_path_info ^(.+\.php)(/.+)$;
fastcgi_pass unix:/run/php/php7.3-fpm.sock; # PHP7.3
fastcgi_index index.php;
include fastcgi_params;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
}
location = /twofactorauth/nginx/auth.php {
fastcgi_split_path_info ^(.+\.php)(/.+)$;
fastcgi_pass unix:/run/php/php7.3-fpm.sock; # PHP7.3
fastcgi_index index.php;
include fastcgi_params;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
fastcgi_param CONTENT_LENGTH "";
}
location /twofactorauth/ {
index index.php;
}
location /twofactorauth/db/ {
deny all;
}
location /transmission {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:9091;
auth_request /twofactorauth/nginx/auth.php;
error_page 401 =401 $scheme://$host/twofactorauth/login/login.php?from=$uri;
proxy_buffering off;
}
}
recharger nginx
1
2
sudo nginx -t
sudo systemctl reload nginx
Lien https://xoyaz.xyz/transmission
saisir utilisateur, mot de passe et le jeton OTP correspondant
Go + Node
Go
Go installation (Debian) , installer la dernière version de Go (https://golang.org/dl/)
1
2
3
4
cd ~
wget https://dl.google.com/go/go1.14.2.linux-amd64.tar.gz
sudo tar -C /usr/local -xzf go1.14.2.linux-amd64.tar.gz
rm go1.14.2.linux-amd64.tar.gz
Environnement de configuration
Bash: ~/.bashrc
1
2
3
echo "export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/go/bin:$HOME/go/bin" >> ~/.bashrc
export "GOPATH=$HOME/go" >> ~/.bashrc
source ~/.bashrc
Nodejs
Installer la version LTS de nodejs pour le frontend.
1
2
sudo apt-get install curl software-properties-common
curl -sL https://deb.nodesource.com/setup_12.x | sudo bash -
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
## Run `sudo apt-get install -y nodejs` to install Node.js 12.x and npm
## You may also need development tools to build native addons:
sudo apt-get install gcc g++ make
## To install the Yarn package manager, run:
curl -sL https://dl.yarnpkg.com/debian/pubkey.gpg | sudo apt-key add -
echo "deb https://dl.yarnpkg.com/debian/ stable main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/yarn.list
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install yarn
Nodejs
1
sudo apt-get install -y nodejs
Wireguard (DESINSTALLE)
Wireguard - base
WireGuard est un serveur VPN à code source ouvert, gratuit, moderne et rapide, doté d’une cryptographie de pointe. Il est plus rapide et plus simple que l’IPSec et l’OpenVPN
Wireguard est dans le noyau 5.6+
1
apt install wireguard
Générer une paire de clés
On se positionne dans le dossier /etc/wireguard/
1
cd /etc/wireguard
WireGuard repose sur une authentification par clé publique/privée (cryptographie asymétrique), vous devez donc créer ces clés avec les sous-commandes wg genkey et wg pubkey
La création de la clé privée se fait avec wg genkey et la clé publique est générée en la canalisant dans wg pubkey
1
umask 077; wg genkey | tee vps70253415-private.key | wg pubkey > vps70253415-public.key
**Autoriser le serveur Wireguard à relayer les paquets **
Autoriser le serveur Wireguard à relayer les paquets venant de ces clients vers l’internet et de traiter les paquets retours (modifier /etc/sysctl.conf)
1
2
3
sed -i 's/^#net.ipv4.ip_forward=1/net.ipv4.ip_forward=1/' /etc/sysctl.conf
sed -i 's/^#net.ipv6.conf.all.forwarding=1/net.ipv6.conf.all.forwarding=1/' /etc/sysctl.conf
sysctl -p # prise en compte immédiate
Fichier de configuration /etc/wireguard/wg0.conf
Récupérer le nom de la carte réseau ip a , dans notre cas eth0
La première étape consiste à choisir une plage IPV4 privée qui sera utilisée par le serveur : 10.19.22.0/8
Pour une adresse IPV6 Local IPv6 Address Generator : fde2:931c:fbc0:b1dc::/64
| Prefix/L | fd |
|---|---|
| Global ID | e2931cfbc0 |
| Subnet ID | b1dc |
| Combine/CID | fde2:931c:fbc0:b1dc::/64 |
| IPv6 addresses | fde2:931c:fbc0:b1dc::/64:XXXX:XXXX:XXXX:XXXX |
| Start Range | fde2:931c:fbc0:b1dc:0:0:0:0 |
| End Range | fde2:931c:fbc0:b1dc:ffff:ffff:ffff:ffff |
| No. of hosts | 18446744073709551616 |
Nous utiliserons 10.19.22.0/24 qui se trouve dans la plage 10.19.22.0/8 . Le serveur aura l’adresse IP suivante: 10.19.22.1 . Il est également nécessaire de choisir un port, qui sera exposé publiquement, pour que le serveur écoute.Le port de documentation standard est généralement 51820.
Créer le fichier /etc/wireguard/wg0.conf
1
nano /etc/wireguard/wg0.conf
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
[Interface]
Address = 10.19.22.1/24
Address = fde2:931c:fbc0:b1dc::1/64
ListenPort = 51820
PostUp = iptables -A FORWARD -i wg0 -j ACCEPT; iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -o eth0 -j MASQUERADE; ip6tables -A FORWARD -i wg0 -j ACCEPT; ip6tables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -o eth0 -j MASQUERADE
PostDown = iptables -D FORWARD -i wg0 -j ACCEPT; iptables -t nat -D POSTROUTING -o eth0 -j MASQUERADE; ip6tables -D FORWARD -i wg0 -j ACCEPT; ip6tables -t nat -D POSTROUTING -o eth0 -j MASQUERADE
PrivateKey = 5Zsr0jQXiuCpHFkye325Zsr0jMUKinVEOPmk=
DNS = 10.19.22.1
DNS = fde2:931c:fbc0:b1dc::1
SaveConfig = true
Address , fixer l’adresse IP privée du serveur à l’intérieur du VPN.Les adresses du réseau VPN de 10.19.22.0 à 10.19.22.255 sont fixées par le masque /24
PostUp , pour la mise en place des règles iptables de translation d’adresses à l’activation du VPN (autoriser le routage des paquets réseau venant des clients vers internet)
PostDown , pour la suppression des règles iptables de translation d’adresses à l’arrêt du VPN
PrivateKey , clé privée du serveur
Modification des droits (lecture uniquement par “root”)
1
chmod 600 /etc/wireguard/wg0.conf
Gestion Wireguard web service
Création dossier application web
1
sudo mkdir -p /opt/appwg
Copier le git wg-gen-web
1
2
3
4
cd ~
git clone https://gitea.cinay.eu/yann/wg-gen-web.git
sudo mkdir -p /usr/local/go/src/wg-gen-web
sudo cp -r wg-gen-web/{api,auth,core,util,version,model,storage,template} /usr/local/go/src/wg-gen-web/
Construction du site
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
cd /home/usernl/wg-gen-web/cmd/wg-gen-web/
go build -o deb-wg-gen-web
cd ../../ui
npm install # + npm audit fix si nécessaire
npm run build
sudo cp /home/usernl/wg-gen-web/cmd/wg-gen-web/deb-wg-gen-web /opt/appwg
sudo mkdir -p /opt/appwg/ui
sudo cp -r /home/usernl/wg-gen-web/ui/dist /opt/appwg/ui/
Configuration .env
l’autorisation à 2 facteurs n’est pas utilisée, le fichier /opt/appwg/.env se résume à remplir la zone correspondante SMTP de la messagerie et désactiver l’autorisation
1
/opt/appwg/.env
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
# IP address to listen to
SERVER=0.0.0.0
# port to bind
PORT=8080
# Gin framework release mode
GIN_MODE=release
# where to write all generated config files
WG_CONF_DIR=/etc/wireguard
# WireGuard main config file name, generally <interface name>.conf
WG_INTERFACE_NAME=wg0.conf
# SMTP settings to send email to clients
SMTP_HOST=smtp.gmail.com
SMTP_PORT=587
SMTP_USERNAME=account@gmail.com
SMTP_PASSWORD=*************
SMTP_FROM=Wg Gen Web <account@gmail.com>
# set provider name to fake to disable auth, also the default
OAUTH2_PROVIDER_NAME=fake
**Créer le service wgweb.service **
Tester manuellement le fonctionnement
Ouvrir un terminal
1
2
3
sudo -s
cd /opt/appwg/
./deb-wg-gen-web # arrêt par Ctrl C
Ouvrir le lien https://wg.rnmkcy.eu
Les échanges sont affichés dans la fenêtre du terminal
Créer un service systemd wgweb qui lance le serveur avec journalisation
1
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/wgweb.service
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
[Unit]
Description=Gestion web wg
After=network.target
[Service]
Type=simple
Restart=on-failure
RestartSec=10
WorkingDirectory=/opt/appwg
ExecStart=/opt/appwg/deb-wg-gen-web
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
wireguard (wg0.conf et server.json)
Modifier les fichiers existants pour être identique au paramétrage de wireguard wg0.conf situé sous /etc/wireguard
1
/etc/wireguard/server.json
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
{
"address": [
"fde2:931c:fbc0:b1dc::1/64",
"10.19.22.1/24"
],
"listenPort": 51820,
"mtu": 0,
"privateKey": "UEQCgh/6a2RQbF9+qqylVjqLCK/mRwqRPc/4vjRsYXg=",
"publicKey": "0s1wsNpuU1RlKgj6AmoN0aKUeb+aESByhO3yTSnfTyE=",
"endpoint": "xoyaz.xyz:51820",
"persistentKeepalive": 16,
"dns": [
"fde2:931c:fbc0:b1dc::1",
"10.19.22.1"
],
"allowedips": [
"0.0.0.0/0",
"::/0"
],
"preUp": "",
"postUp": "iptables -A FORWARD -i wg0 -j ACCEPT; iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -o eth0 -j MASQUERADE; ip6tables -A FORWARD -i wg0 -j ACCEPT; ip6tables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -o eth0 -j MASQUERADE",
"preDown": "",
"postDown": "iptables -D FORWARD -i wg0 -j ACCEPT; iptables -t nat -D POSTROUTING -o eth0 -j MASQUERADE; ip6tables -D FORWARD -i wg0 -j ACCEPT; ip6tables -t nat -D POSTROUTING -o eth0 -j MASQUERADE",
"updatedBy": "Unknown",
"created": "2020-06-29T12:31:50.589913433Z",
"updated": "2020-06-29T12:31:50.589913433Z"
1
cat /etc/wireguard/wg0.conf
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
[Interface]
Address = fde2:931c:fbc0:b1dc::1/64
Address = 10.19.22.1/24
ListenPort = 51820
PrivateKey = UEQCgh/6a2RQbF9+qqylVjqLCK/mRwqRPc/4vjRsYXg=
PreUp = echo WireGuard PreUp
PostUp = echo WireGuard PostUp
PreDown = echo WireGuard PreDown
}
On modifie dans /opt/appwg/.env ,le paramètre WG_CONF_DIR=./wireguard → WG_CONF_DIR=/etc/wireguard
Recharger systemd puis démarrer le service:
1
2
3
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl start wgweb.service
sudo systemctl status wgweb.service
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
● wgweb.service - Gestion web wg
Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/wgweb.service; disabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Mon 2020-06-29 12:16:29 CEST; 83ms ago
Main PID: 2084 (deb-wg-gen-web)
Tasks: 5 (limit: 1146)
Memory: 8.7M
CGroup: /system.slice/wgweb.service
└─2084 /opt/appwg/deb-wg-gen-web
Jun 29 12:16:29 vps70253415 systemd[1]: Started Gestion web wg.
Jun 29 12:16:29 vps70253415 deb-wg-gen-web[2084]: time="2020-06-29T12:16:29+02:00" level=info msg="Lancement de la version Web de Wg Gen : yann"
Jun 29 12:16:29 vps70253415 deb-wg-gen-web[2084]: time="2020-06-29T12:16:29+02:00" level=warning msg="Oauth n'est pas utilisé, aucune authentification réelle ne sera effectuée"
Activer le service si tout fonctionne
1
sudo systemctl enable wgweb.service
Activer serveur wireguard
Le gestionnaire web est à jour , on peut lancer le serveur wireguard
1
sudo systemctl start wg-quick@wg0.service
Vérifier
1
systemctl status wg-quick@wg0.service
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
● wg-quick@wg0.service - WireGuard via wg-quick(8) for wg0
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/wg-quick@.service; disabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (exited) since Mon 2020-06-29 13:54:19 CEST; 9s ago
Docs: man:wg-quick(8)
man:wg(8)
https://www.wireguard.com/
https://www.wireguard.com/quickstart/
https://git.zx2c4.com/wireguard-tools/about/src/man/wg-quick.8
https://git.zx2c4.com/wireguard-tools/about/src/man/wg.8
Process: 3171 ExecStart=/usr/bin/wg-quick up wg0 (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 3171 (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Jun 29 13:54:19 vps70253415 wg-quick[3171]: [#] echo WireGuard PreUp
Jun 29 13:54:19 vps70253415 wg-quick[3171]: WireGuard PreUp
Jun 29 13:54:19 vps70253415 wg-quick[3171]: [#] ip link add wg0 type wireguard
Jun 29 13:54:19 vps70253415 wg-quick[3171]: [#] wg setconf wg0 /dev/fd/63
Jun 29 13:54:19 vps70253415 wg-quick[3171]: [#] ip -6 address add fde2:931c:fbc0:b1dc::1/64 dev wg0
Jun 29 13:54:19 vps70253415 wg-quick[3171]: [#] ip -4 address add 10.19.22.1/24 dev wg0
Jun 29 13:54:19 vps70253415 wg-quick[3171]: [#] ip link set mtu 1420 up dev wg0
Jun 29 13:54:19 vps70253415 wg-quick[3171]: [#] echo WireGuard PostUp
Jun 29 13:54:19 vps70253415 wg-quick[3171]: WireGuard PostUp
Jun 29 13:54:19 vps70253415 systemd[1]: Started WireGuard via wg-quick(8) for wg0.
Activer
1
sudo systemctl enable wg-quick@wg0.service
WireGuard modifications via systemd.path
Appliquer automatiquement les modifications apportées à WireGuard
Utilisation de systemd.path monitor pour les changements dans le répertoire, voir systemd doc
1
/etc/systemd/system/wg-gen-web.path
[Unit]
Description=Surveiller /etc/wireguard pour les changements
[Path]
PathModified=/etc/wireguard
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
Ce wg-gen-web.path activera le fichier de l’unité avec le même nom, wg-gen-web.service
1
/etc/systemd/system/wg-gen-web.service
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
[Unit]
Description=Relancer WireGuard si changements
After=network.target
[Service]
Type=oneshot
ExecStart=/usr/bin/systemctl restart wg-quick@wg0.service
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
Ce qui permettra de relancer le service WireGuard
1
2
sudo systemctl start wg-gen-web.path
sudo systemctl status wg-gen-web.path
1
2
3
4
5
6
● wg-gen-web.path - Surveiller /etc/wireguard pour les changements
Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/wg-gen-web.path; disabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (waiting) since Mon 2020-06-29 13:55:51 CEST; 23ms ago
Jun 29 13:55:51 vps70253415 systemd[1]: Started Surveiller /etc/wireguard pour les changements.
Activation
1
sudo systemctl enable wg-gen-web.path
Pour suivre dans le journal
1
sudo journalctl -f -t wg-quick
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
-- Logs begin at Mon 2020-06-29 11:14:09 CEST. --
Jun 29 13:59:54 vps70253415 wg-quick[3479]: [#] ip link add wg0 type wireguard
Jun 29 13:59:54 vps70253415 wg-quick[3479]: [#] wg setconf wg0 /dev/fd/63
Jun 29 13:59:54 vps70253415 wg-quick[3479]: [#] ip -6 address add fde2:931c:fbc0:b1dc::1/64 dev wg0
Jun 29 13:59:54 vps70253415 wg-quick[3479]: [#] ip -4 address add 10.19.22.1/24 dev wg0
Jun 29 13:59:54 vps70253415 wg-quick[3479]: [#] ip link set mtu 1420 up dev wg0
Jun 29 13:59:54 vps70253415 wg-quick[3479]: [#] iptables -A FORWARD -i wg0 -j ACCEPT; iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -o eth0 -j MASQUERADE; ip6tables -A FORWARD -i wg0 -j ACCEPT; ip6tables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -o eth0 -j MASQUERADE
Gestionnaire web wireguard via SSH
Wireguard → localhost:8080
Ouvrir un terminal sur le client linux qui dispose des clés ssh et lancer la commande
1
ssh -L 9000:localhost:8080 usernl@5.2.79.127 -p 55036 -i /home/yannick/.ssh/OVZ-STORAGE-128
Ouvrir un navigateur sur le client et saisir localhost:9000 pour afficher le gestionnaire web de wireguard
wg.xoyaz.xyz
Accès paramétrage wireguard serveur et client par lien https://wg.xoyaz.xyz
Ajouter le sous-domaine wg au gestionnaire de domaine xoyaz.xyz
Créer un certificat “let’s Encrypt” pour le sous-domaine wg.xoyaz.xyz
Utiliser Github comme accès sécurisé
Créer un accès sécurisé oauth2 via github (Creating an OAuth App)
Se connecter sur github en utilisateur puis Settings → Developer settings
Nom de l’application : wireguard-xoyaz.xyz
URL de redirection : https://wg.xoyaz.xyz
Sauvegarder ID et Secret du client pour la configuration du .env puis cliquer sur Enregistrer
Le fichier /opt/appwg/.env complet après les modifications
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
# IP address to listen to
SERVER=127.0.0.1
# port to bind
PORT=8080
# Gin framework release mode
GIN_MODE=release
# where to write all generated config files
WG_CONF_DIR=/etc/wireguard
# WireGuard main config file name, generally <interface name>.conf
WG_INTERFACE_NAME=wg0.conf
# SMTP settings to send email to clients
SMTP_HOST=cinay.eu
SMTP_PORT=587
SMTP_USERNAME=wg@cinay.eu
SMTP_PASSWORD=xxxxxxxxxxx
SMTP_FROM=Wg Gen Web <wg@cinay.eu>
# set provider name
OAUTH2_PROVIDER_NAME=github
OAUTH2_PROVIDER=https://github.com
OAUTH2_CLIENT_ID=xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
OAUTH2_CLIENT_SECRET=xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
OAUTH2_REDIRECT_URL=https://wg.xoyaz.xyz
Relancer le service sudo systemctl restart wgweb.service
Fichier de configuration /etc/nginx/conf.d/wg.xoyaz.xyz.conf
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
server {
listen 443 ssl http2;
listen [::]:443 ssl http2;
server_name wg.xoyaz.xyz;
ssl_certificate /etc/ssl/private/xoyaz.xyz-fullchain.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/ssl/private/xoyaz.xyz-key.pem;
# TLS 1.3 only
ssl_protocols TLSv1.3;
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers off;
# HSTS (ngx_http_headers_module is required) (63072000 seconds)
add_header Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=63072000" always;
# OCSP stapling
ssl_stapling on;
ssl_stapling_verify on;
# verify chain of trust of OCSP response using Root CA and Intermediate certs
ssl_trusted_certificate /etc/ssl/private/xoyaz.xyz-fullchain.pem;
# replace with the IP address of your resolver
resolver 127.0.0.1;
location / {
#//normal proxy configuration
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_pass_request_headers on;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header Accept-Encoding "";
proxy_pass http://localhost:8080;
proxy_redirect default;
}
}
Recharger nginx sudo systemctl reload nginx
Accès https://wg.xoyaz.xyz
Authentication 2FA (login+ mot de passe+jeton TOTP)
A l’aide de nginx et PHP, on va sécuriser l’accès au paramétrage wireguard
Le fichier de configurarion wireguard web /opt/appwg/.env complet
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
# IP address to listen to
SERVER=127.0.0.1
# port to bind
PORT=8080
# Gin framework release mode
GIN_MODE=release
# where to write all generated config files
WG_CONF_DIR=/etc/wireguard
# WireGuard main config file name, generally <interface name>.conf
WG_INTERFACE_NAME=wg0.conf
# SMTP settings to send email to clients
SMTP_HOST=cinay.eu
SMTP_PORT=587
SMTP_USERNAME=wg@cinay.eu
SMTP_PASSWORD=xxxxxxxxxxx
SMTP_FROM=Wg Gen Web <wg@cinay.eu>
# set provider name to fake to disable auth, also the default
OAUTH2_PROVIDER_NAME=fake
Relancer le service sudo systemctl restart wgweb.service
Fichier de configuration /etc/nginx/conf.d/wg.xoyaz.xyz.conf
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
server {
listen 443 ssl http2;
listen [::]:443 ssl http2;
server_name wg.xoyaz.xyz;
ssl_certificate /etc/ssl/private/xoyaz.xyz-fullchain.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/ssl/private/xoyaz.xyz-key.pem;
root /var/www/;
index index/ index.php;
# TLS 1.3 only
ssl_protocols TLSv1.3;
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers off;
# HSTS (ngx_http_headers_module is required) (63072000 seconds)
add_header Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=63072000" always;
# OCSP stapling
ssl_stapling on;
ssl_stapling_verify on;
# verify chain of trust of OCSP response using Root CA and Intermediate certs
ssl_trusted_certificate /etc/ssl/private/xoyaz.xyz-fullchain.pem;
# replace with the IP address of your resolver
resolver 127.0.0.1;
location = /twofactorauth/login/login.php {
allow all;
auth_request off;
fastcgi_split_path_info ^(.+\.php)(/.+)$;
fastcgi_pass unix:/run/php/php7.3-fpm.sock; # PHP7.3
fastcgi_index index.php;
include fastcgi_params;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
}
location = /twofactorauth/nginx/auth.php {
fastcgi_split_path_info ^(.+\.php)(/.+)$;
fastcgi_pass unix:/run/php/php7.3-fpm.sock; # PHP7.3
fastcgi_index index.php;
include fastcgi_params;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
fastcgi_param CONTENT_LENGTH "";
}
location /twofactorauth/ {
index index.php;
}
location /twofactorauth/db/ {
deny all;
}
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:8080;
auth_request /twofactorauth/nginx/auth.php;
error_page 401 =401 $scheme://$host/twofactorauth/login/login.php?from=$uri;
proxy_buffering off;
}
}
Recharger nginx sudo systemctl reload nginx
Accès https://wg.xoyaz.xyz
Saisir login + mot de passe + Jeton TOTP
DNS Unbound
Un problème majeur avec beaucoup de configurations VPN est que le DNS n’est pas suffisant. Cela finit par une fuite de connexion client et de détails d’emplacement. Un bon moyen de tester cela est à travers le site http://dnsleak.com/
Nous allons sécuriser le trafic DNS avec la solution unbound qui offre les caractéristiques suivantes
- Léger et rapide
- Facile à installer et à configurer
- Orienté sécurité
- Prise en charge DNSSEC
Nous allons le configurer de manière à contrer les fuites DNS, les attaques plus sophistiquées comme la fausse configuration de proxy, les routeurs escrocs et toutes sortes d’attaques MITM sur HTTPS et autres protocoles.
Nous installons unbound sur le serveur
Passage en mode super utilisateur
1
sudo -s # ou su
ATTENTION : Le programme resolvconf est en général seulement nécessaire quand un système a plusieurs programmes qui ont besoin de modifier de façon dynamique les informations sur les serveurs de noms de domaine. Sur un système simple où les serveurs de noms de domaine ne changent pas souvent ou bien ne sont modifiés que par un programme, le fichier de configuration **resolv.conf** est suffisant.
Il faut installer resolvconf, sinon on a une erreur unbound-resolvconf
Une fois le paquet « resolvconf » installé, il ne faut plus modifier le fichier « /etc/resolv.conf », car le contenu de celui-ci sera automatiquement géré et remplacé par « resolvconf ».
Installation des outils dns, des paquets Unbound et resolv :
1
apt install unbound unbound-host resolvconf -y
Téléchargement de la liste des serveurs DNS racines
1
2
curl -o /var/lib/unbound/root.hints https://www.internic.net/domain/named.cache
chown unbound:unbound /var/lib/unbound/root.hints
Ajout d’un fichier de configuration dns-vps70253415.conf
1
/etc/unbound/unbound.conf.d/dns-vps70253415.conf
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
server:
num-threads: 4
# enable logs
verbosity: 0 # no verbosity, only errors
# liste des serveurs DNS racine
root-hints: "/var/lib/unbound/root.hints"
# Répondre aux requêtes DNS sur toutes les interfaces
interface: 0.0.0.0 # 0.0.0.0 unbound sur plusieurs interfaces
interface: ::0
max-udp-size: 3072
# IPs authorised to access the DNS Server
access-control: 0.0.0.0/0 refuse
access-control: 127.0.0.0/8 allow
access-control: 10.19.22.0/16 allow
access-control: ::0/0 refuse
access-control: ::1 allow
access-control: ::ffff:127.0.0.1 allow
access-control: fe80::/10 allow
access-control: fde2:931c:fbc0:b1dc::/48 allow
local-zone: "19.10.in-addr.arpa." transparent
#hide DNS Server info
hide-identity: yes
hide-version: yes
# limit DNS fraud and use DNSSEC
harden-glue: yes
harden-dnssec-stripped: yes
harden-referral-path: yes
# add an unwanted reply threshold to clean the cache and avoid, when possible, DNS poisoning
unwanted-reply-threshold: 10000000
# have the validator print validation failures to the log
val-log-level: 1
# minimum lifetime of cache entries in seconds
cache-min-ttl: 1800
# maximum lifetime of cached entries in seconds
cache-max-ttl: 14400
prefetch: yes
prefetch-key: yes
#include: /etc/unbound/unbound.conf.d/adslist.txt
Droits
1
chown -R unbound:unbound /var/lib/unbound
Pour vérifier si le fichier de configuration est valide
1
unbound-checkconf /etc/unbound/unbound.conf.d/dns-vps70253415.conf
unbound-checkconf: no errors in /etc/unbound/unbound.conf.d/dns-vps70253415.conf
Désactiver systemd-resolved (si utilisé)
1
2
systemctl stop systemd-resolved
systemctl disable systemd-resolved
Activer Unbound (ILS SONT ACTIFS DES LEUR INSTALLATION)
1
2
systemctl enable unbound-resolvconf
systemctl enable unbound
Redémarrer le serveur
1
systemctl reboot
Après redémarrage et connexion au serveur
1
systemctl status unbound unbound-resolvconf resolvconf
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
● unbound.service - Unbound DNS server
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/unbound.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Mon 2020-06-29 10:30:54 CEST; 51s ago
Docs: man:unbound(8)
Process: 419 ExecStartPre=/usr/lib/unbound/package-helper chroot_setup (code=exited, status=0/SU
Process: 427 ExecStartPre=/usr/lib/unbound/package-helper root_trust_anchor_update (code=exited,
Main PID: 479 (unbound)
Tasks: 4 (limit: 1146)
Memory: 27.4M
CGroup: /system.slice/unbound.service
└─479 /usr/sbin/unbound -d
● unbound-resolvconf.service - Unbound DNS server via resolvconf
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/unbound-resolvconf.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled
Active: active (exited) since Mon 2020-06-29 10:30:54 CEST; 51s ago
Process: 483 ExecStart=/usr/lib/unbound/package-helper resolvconf_start (code=exited, status=0/S
Main PID: 483 (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
● resolvconf.service - Nameserver information manager
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/resolvconf.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (exited) since Mon 2020-06-29 10:30:49 CEST; 56s ago
Docs: man:resolvconf(8)
Process: 159 ExecStartPre=/bin/mkdir -p /run/resolvconf/interface (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS
Process: 164 ExecStartPre=/bin/touch /run/resolvconf/postponed-update (code=exited, status=0/SUC
Process: 170 ExecStart=/sbin/resolvconf --enable-updates (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Vérifications
Les commandes suivantes ne fonctionneront que si le paquet “dnsutils” est installé sur votre système Debian!
On teste en utilisant les serveurs DNS locaux
1
dig @127.0.0.1 afnic.fr +short +dnssec
1
2
192.134.5.37
A 13 2 600 20200727092903 20200627041243 49517 afnic.fr. bjYXQtVXcDZeY9GbpF7mRxyDacpSRyu2fbgwx//9FudaejAP7xl+BEyp rMTimYAKqC7IUErlK6jpoj9D4EGPfA==
Mise à jour des serveurs DNS racines
Télécharger le script
1
curl -o /etc/unbound/dnsunbound-update-root-dns.sh https://yann.cinay.eu/files/dnsunbound-update-root-dns.sh
Droits en exécution pour le bash dnsunbound-update-root-dns.sh
1
chmod +x /etc/unbound/dnsunbound-update-root-dns.sh
Planification journalière
1
crontab -e
Ajouter en fin de fichier
1
2
# Mise à jour automatique des serveurs DNS de la racine
10 02 * * * /etc/unbound/dnsunbound-update-root-dns.sh > /dev/null
Serveur Audio Gonic
Installation gonic
Le dossier de l’application
1
sudo mkdir -p /opt/gonic
Le dossier musique est local /home/usernl/backup/musique, créer un lien sur ce dossier
1
sudo ln -s /home/usernl/backup/musique /opt/gonic/music
Installer “gonic”
1
2
3
4
5
6
# dépendances
sudo apt install build-essential git sqlite libtag1-dev ffmpeg libasound2-dev pkg-config
cd $HOME/
# cloner
git clone https://gitea.cinay.eu/yann/golang-subsonic.git
cd golang-subsonic/
Construire l’exécutable “gonic” et le copier dans /usr/local/bin
1
2
./_do_build_server
sudo mv gonic /usr/local/bin/
Service gonic
Que fait le service ?
- Le dossier musique ets local
- lancer le serveur “gonic” en écoute local sur le port 4747 avec les options
-music-path,-db-pathet-proxy-prefix - A l’arrêt,tuer la tâche “gonic”
Chaque service généré par systemd est configuré par un fichier .service qui se trouve dans le répertoire /etc/systemd/system
1
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/gonic.service
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
[Unit]
Description=Gonic audio server
After=network.target
[Service]
Type=simple
Restart=on-failure
RestartSec=10
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/gonic -music-path /opt/gonic/music -db-path /opt/gonic/gonic.db -proxy-prefix /
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
Recharger systemd puis démarrer le service:
1
2
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl start gonic.service
Visualiser le journal
1
sudo journalctl -t gonic
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
-- Logs begin at Mon 2020-06-29 11:14:09 CEST, end at Mon 2020-06-29 15:57:28 CEST. --
Jun 29 15:57:28 vps70253415 gonic[12048]: 2020/06/29 15:57:28 starting gonic v0.8.8
Jun 29 15:57:28 vps70253415 gonic[12048]: 2020/06/29 15:57:28 provided config
Jun 29 15:57:28 vps70253415 gonic[12048]: 2020/06/29 15:57:28 cache-path /tmp/gonic_cache
Jun 29 15:57:28 vps70253415 gonic[12048]: 2020/06/29 15:57:28 config-path
Jun 29 15:57:28 vps70253415 gonic[12048]: 2020/06/29 15:57:28 db-path /opt/gonic/gonic.db
Jun 29 15:57:28 vps70253415 gonic[12048]: 2020/06/29 15:57:28 jukebox-enabled false
Jun 29 15:57:28 vps70253415 gonic[12048]: 2020/06/29 15:57:28 listen-addr 0.0.0.0:4747
Jun 29 15:57:28 vps70253415 gonic[12048]: 2020/06/29 15:57:28 music-path /opt/gonic/music
Jun 29 15:57:28 vps70253415 gonic[12048]: 2020/06/29 15:57:28 proxy-prefix /
Jun 29 15:57:28 vps70253415 gonic[12048]: 2020/06/29 15:57:28 scan-interval 0
Jun 29 15:57:28 vps70253415 gonic[12048]: 2020/06/29 15:57:28 version false
Jun 29 15:57:28 vps70253415 gonic[12048]: 2020/06/29 15:57:28 starting job 'http'
Accès web
Via SSH
- Gonic → localhost:4747
on va utiliser une redirection de port via ssh
Serveur audio gonic
Ouvrir un terminal sur le client linux qui dispose des clés ssh et lancer la commande
1
ssh -L 9500:localhost:4747 usernl@5.2.79.127 -p 55036 -i /home/yannick/.ssh/OVZ-STORAGE-128
Ouvrir un navigateur sur le client et saisir localhost:9500 pour afficher le serveur audio gonic
Proxy nginx zic.xoyaz.xyz
Gonic est un serveur local http sur le port 4747 et pour un accès externe il nous faut un proxy
Proxy nginx - configuration /etc/nginx/conf.d/zic.xoyaz.xyz.conf
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
# /etc/nginx/conf.d/zic.xoyaz.xyz.conf
##
# Virtual Host zic.xoyaz.xyz
##
server {
listen 80;
listen [::]:80;
## redirect http to https ##
server_name zic.xoyaz.xyz;
return 301 https://$server_name$request_uri;
}
server {
listen 443 ssl http2;
listen [::]:443 ssl http2;
server_name zic.xoyaz.xyz;
ssl_certificate /etc/ssl/private/xoyaz.xyz-fullchain.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/ssl/private/xoyaz.xyz-key.pem;
root /var/www/;
index index/ index.htm index.nginx-debian/;
# TLS 1.3 only
ssl_protocols TLSv1.3;
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers off;
# HSTS (ngx_http_headers_module is required) (63072000 seconds)
add_header Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=63072000" always;
# OCSP stapling
ssl_stapling on;
ssl_stapling_verify on;
# verify chain of trust of OCSP response using Root CA and Intermediate certs
ssl_trusted_certificate /etc/ssl/private/xoyaz.xyz-fullchain.pem;
# replace with the IP address of your resolver
resolver 127.0.0.1;
# Proxy audio gonic server
location / {
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
proxy_pass http://localhost:4747;
proxy_read_timeout 120;
}
}
On vérifie et on relance le serveur nginx
1
2
sudo nginx -t
sudo systemctl reload nginx
Accès https://zic.xoyaz.xyz